Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a condition where the blood vessels lose their flexibility and become hardened.
Major causes include:
・Diabetes
・Alcohol consumption, smoking
・Obesity, aging, stress
These factors can lead to vascular endothelial cell damage, resulting in loss of vascular flexibility and atherosclerosis. As the condition progresses, blood vessels narrow, leading to blockages caused by blood clots, which may result in conditions such as stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, and myocardial infarction.
Therefore, our clinic offers treatment using adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy, a regenerative medicine approach. Stem cells are isolated from a very small amount of adipose tissue, typically 4-5 cm^3, and then cultured and multiplied up to approximately 100 million cells at our affiliated Cell Processing Center (CPC). These stem cells are then administered via intravenous drip or injection. Our unique method allows for minimally invasive and highly safe treatment, as we use a proprietary technique to extract very small amounts of adipose tissue.

Candidates for treatment
- Those judged to have arteriosclerotic lesions
- Those with a history of myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, or stroke
- Those with plaques (IMT ≥ 1.1) in the carotid arteries (common carotid artery, internal carotid artery) as determined by carotid artery echo examination
- Those with coronary artery wall irregularities, calcification, stenosis, or occlusion as detected by coronary artery CT examination
- Those with cerebral infarction lesions identified by head MRI or MRA examination
- Those with two or more second-degree blood relatives with arteriosclerotic diseases
- Those judged to have a high risk of arteriosclerosis based on genetic testing
Ineligible individuals for treatment
- Individuals under 18 years of age at the time of application
- Those in poor health who cannot withstand fat extraction
- Those who lack the capacity to provide informed consent or whose consent cannot be obtained from a surrogate
- Those who have not accepted the informed consent document for this treatment and have not provided written consent after receiving sufficient explanation and freely expressing their consent (or whose surrogate has not consented in writing)
- Those determined by the attending physician to be ineligible for treatment based on interviews, examinations, etc.
- Pregnant individuals
- Those undergoing treatment for gynecological conditions
- Those diagnosed with proliferative diabetic retinopathy or age-related macular degeneration
- Those with poorly controlled hypertension or arrhythmias
- Those showing clinical symptoms of delirium
- Those with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity
- Those currently undergoing treatment for or hospitalized within the past 3 months for cerebrovascular disorders such as cerebral infarction, intracerebral hemorrhage, or subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Those currently undergoing treatment for or untreated depression, or those with depression that has not improved with treatment
- Those with positive results in infection tests such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, or syphilis within the past 12 weeks.
※For more details, please contact us by phone or email.
Benefits of adipose-derived stem cell therapy
1.Using one’s own adipose-derived stem cells results in fewer side effects and ensures safety.
Since no drugs or chemicals are used, you can undergo treatment with peace of mind.

2.No hospitalization or surgery is required.
Adipose stem cell therapy can be performed on an outpatient basis, both for adipose tissue harvesting and autologous adipose-derived stem cell administration.
It is a minimally invasive treatment with minimal physical burden.
3.Storing stem cells allows for lifelong treatment.
It is also possible to store cultured stem cells for future injections.
Treatment process
Treatment can be done on an outpatient basis without hospitalization.
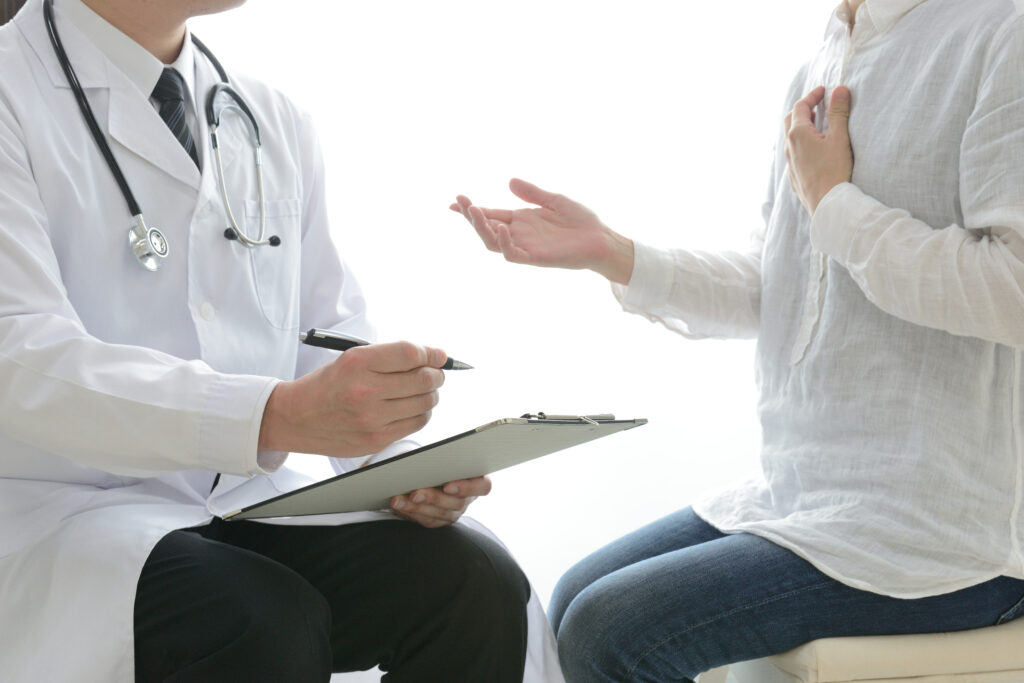
STEP01
Counseling
Explanation and consent, exchanged in writing.

↓
STEP02
Blood test
Conduct preliminary testing and suitability assessment.
↓
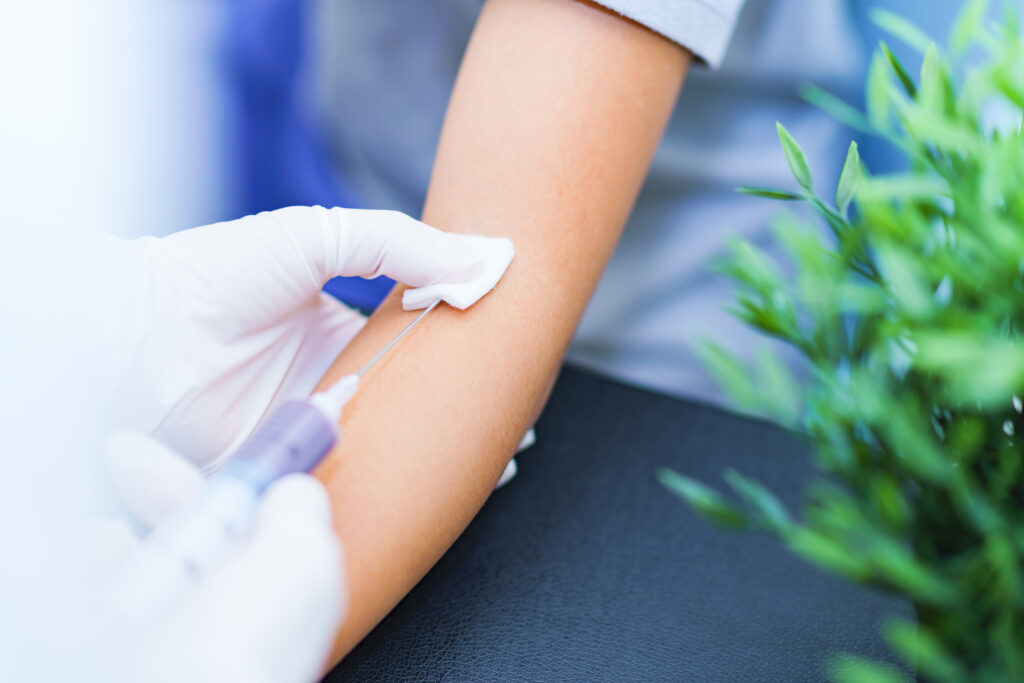
STEP03
Fat extraction and blood sampling
Fat extraction (about the size of two grains of rice) is performed from a location on the abdomen or similar where fat can be reliably collected under local anesthesia. Blood sampling of 100ml is conducted for cultivation purposes.
↓
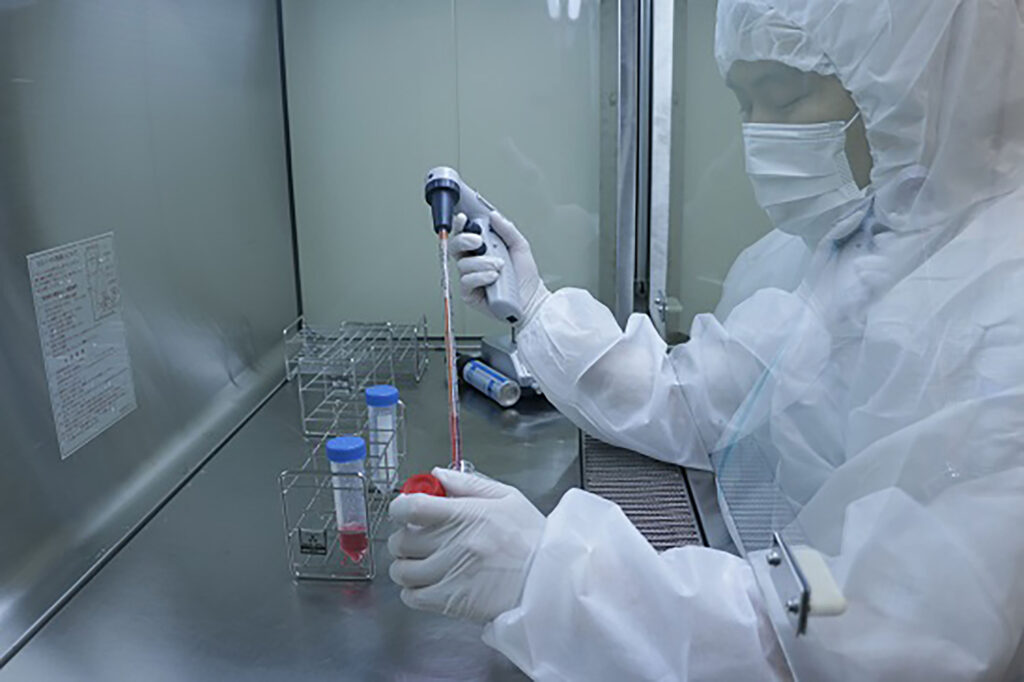
STEP04
Cell culture and proliferation at the CPC (Cultivation Facility)
※Cells are cultured for approximately 6 to 8 weeks with the aim of cultivating 100 million cells.※There may be individual differences in the amount of cell proliferation.

↓
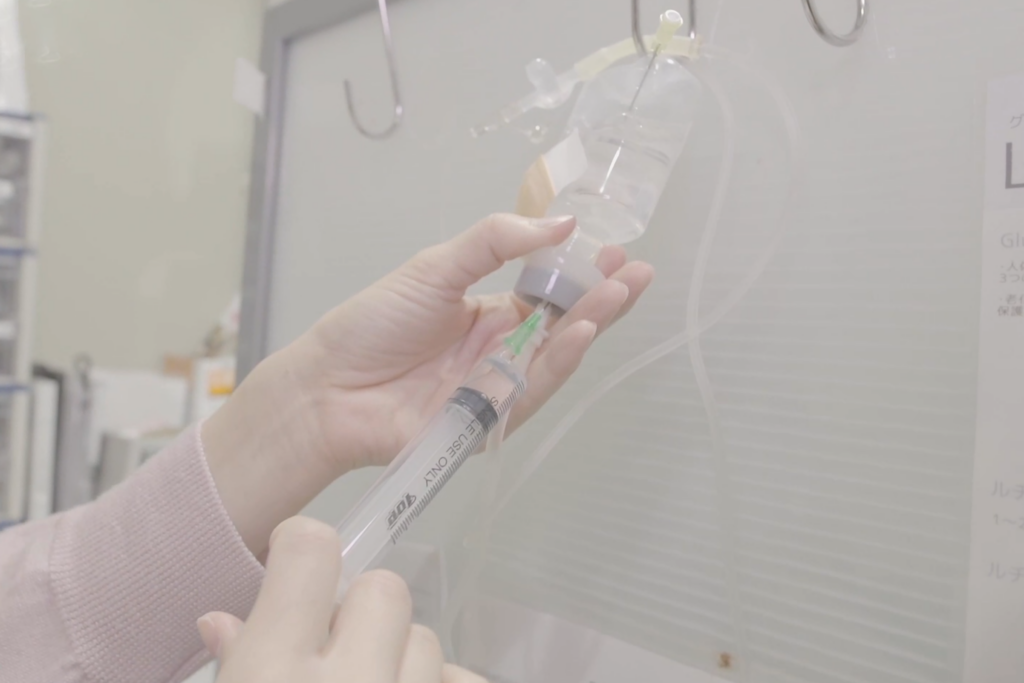
STEP05
Administration via drip (approximately 30 minutes)
The cultured stem cells are administered via drip.
↓
STEP06
Follow-up Observation
We aim to observe as closely as possible at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after stem cell administration.
Expected Effects and Potential Side Effects
Expected Effects
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells are capable of differentiating (acquiring morphology and function) into nerve, fat, muscle, bone, cartilage, and other visceral tissues, enabling the repair of damaged or aging cells.
Additionally, soluble factors such as cytokines and exosomes released from stem cells exert paracrine effects, leading to various therapeutic effects including immune modulation, angiogenesis, anti-inflammatory effects, antioxidative effects, anti-apoptotic effects, and tissue repair effects.
Possible Side Effects
【During Adipose Tissue Harvesting】
- Bleeding from the incision site
- Infection or pain at the incision site
- Side effects of anesthesia use, allergic reactions (palpitations, hives, difficulty breathing, etc.)
【Adverse Effects during Administration】
- Fever after stem cell infusion Usually resolves within 24 hours.
- Allergic reactions Reports of allergic symptoms such as palpitations, hives, and difficulty breathing during treatment.
- Unexpected Adverse Events There have been cases where patients who received adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy died from pulmonary embolism. The causal relationship between stem cell administration and death from pulmonary embolism is unclear, but pulmonary embolism is the most dangerous complication of intravenous stem cell administration.
In the event that pulmonary embolism occurs during the course of treatment, the clinic will respond as follows
①If it occurs within the clinic, severity will be assessed based on the guidelines for the treatment of pulmonary embolism, and immediate respiratory and circulatory management will be implemented. Subsequently, the patient will be promptly transported to a collaborating medical institution.
②If symptoms such as sudden difficulty breathing, chest pain, or cold sweats occur outside the clinic, patients are instructed to contact the clinic by phone. The clinic will assess the need for emergency assistance and provide guidance on appropriate hospitals, including collaborating medical institutions, if necessary.
③Regarding adverse events, the clinic will initially handle the situation. Therefore, if patients experience any concerning symptoms after stem cell infusion, they are requested to contact the clinic (or the emergency contact line outside of business hours). If symptoms arise that cannot be managed at the clinic, arrangements will be made for referral to an external medical facility equipped with hospitalization facilities.
Points to Note in this Treatment
Please refrain from vigorous exercise, staying up all night, and excessive alcohol consumption on the day of administration.
Storage and Disposal of Samples
The blood collected in this treatment will be used solely for the patient’s own treatment. If treatment results are to be used for research purposes, separate confirmation will be obtained from the patient or their proxy regarding the use. Additionally, no information identifying you or your individual data will be disclosed, including for the purpose of announcing treatment results. A portion of the collected and cultured cell products will be stored at -80 degrees Celsius for a minimum of 10 years prior to each treatment session.
In Case of Cultivation Failure
During fat collection or during the cultivation of autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells, it is extremely rare but possible for contamination to occur, such as with bacteria or fungi. If contamination is confirmed, all cultured cells must be discarded, and administration cannot proceed. In such cases, the materials will be discarded. If you still wish to continue treatment under these circumstances, a new fat tissue collection will be required. ※In such cases, there will be no charge for the collection.
Review and Notification of This Treatment
In accordance with the Act on the Safety of Regenerative Medicine, the treatment using autologous adipose-derived stem cells conducted at our clinic undergoes examination by the Committee on Regenerative Medicine, and upon approval of “appropriate,” a regenerative medicine provision plan is submitted to the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare. If you wish to view the plan, please contact the inquiry desk.
Comparison with other treatment methods
Arteriosclerosis is known to be influenced by various factors, and the treatment approach varies depending on the underlying conditions. Generally, lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and exercise are prioritized, and if improvement is not observed, pharmacotherapy or surgical interventions may be recommended.
Dietary therapy involves adopting a balanced and nutritious diet, limiting excessive alcohol intake, and maintaining a regular eating pattern. Exercise therapy typically includes activities like walking or swimming for at least 30 minutes, 3 to 4 days per week.
If lifestyle modifications do not lead to improvement, pharmacotherapy options such as statins to lower cholesterol, fibrates to reduce triglyceride production in the liver and increase cholesterol excretion, and omega-3 fatty acid supplements to lower triglycerides and promote blood thinning may be prescribed.
Pharmacotherapy carries the risk of side effects due to continuous use. In some cases, catheter-based treatments or bypass surgery may be chosen to improve narrowed or blocked blood vessels. These surgical interventions are more invasive treatment methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is hospitalization necessary?
A: While it is necessary to visit our clinic twice for the collection of patient’s own tissues and for the administration of the cultured cells, both procedures can be done on an outpatient basis.
Q: How long does the treatment take?
A: The collection of patient’s own tissues takes about 1 hour, and the treatment itself via intravenous drip takes around 1 to 2 hours to complete. Since we operate on an appointment-only basis, there is no waiting time. However, please note that it takes approximately 6 to 8 weeks for the cultivation of adipose stem cells. Therefore, the entire process from the initial consultation to the treatment may take about 1.5 to 2 months.
Q: How much of my own tissue is needed for the treatment?
A: Approximately 3mm in diameter and 5mm in depth of tissue is collected from the skin surface. The procedure is performed under anesthesia, so there is minimal discomfort.
Q: How much of my own tissue is needed for the treatment?
A: About 20mL of tissue is collected, which is slightly more than a tablespoon. Even individuals who are thin or elderly can undergo the procedure.
Q: Is safety ensured?
A: Treatment through regenerative medicine requires the submission of a treatment plan to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and it must be accepted before it can be provided. Our clinic’s application has been accepted, and we offer treatments that have undergone rigorous safety scrutiny domestically.
Q: Is it eligible for medical expense deduction?
A: Depending on the purpose of treatment, it may be eligible for medical expense deduction. For details on the procedure, please contact your nearest tax office.


