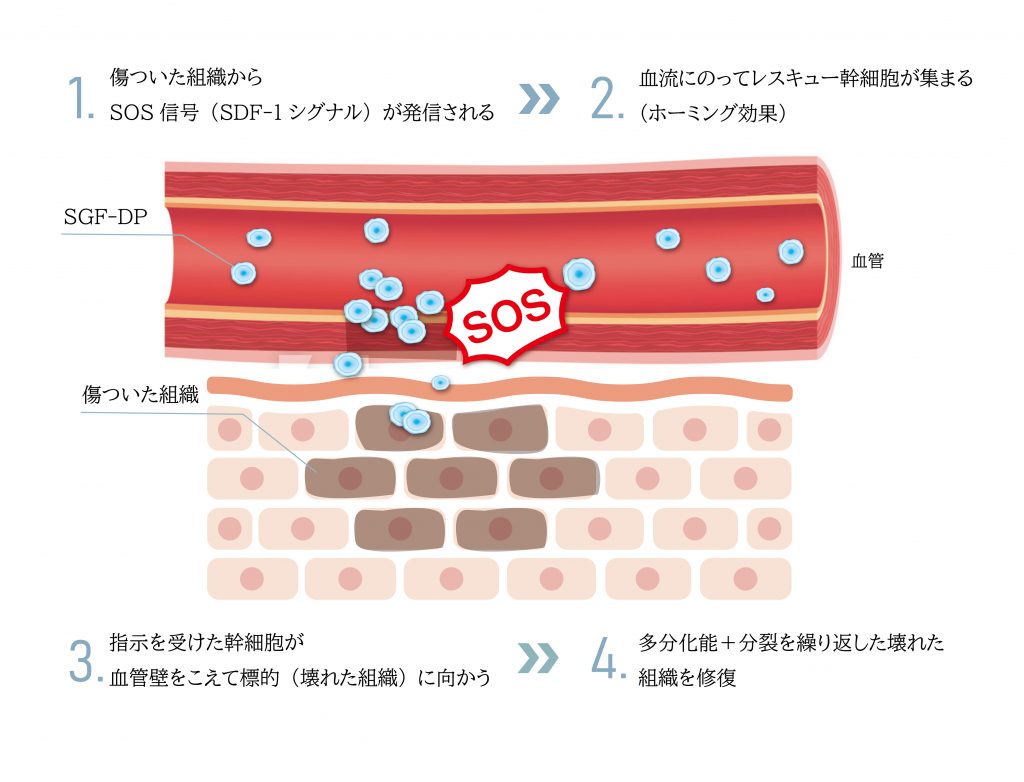
Stem cells have the ability called “homing”. The human body consists of about 200 types and 37 trillion cells, which are replaced daily and are damaged by injuries, illnesses, aging, and so on. However, these cells have the ability to revive them and replenish tissues lost due to diseases, accidents, and aging. Stem cells act like a rescue team for the body. One of the major characteristics of stem cells is their ability to divide into stem cells with the same capabilities (“self-renewal ability”) and to differentiate into various cells such as blood and skin that make up the body (“differentiation ability”). At birth, there are about 10 billion stem cells in the body, but this number decreases with age, and by the age of 60, it is said that there are only about 200 million left. As the number of precious stem cells decreases, the body becomes unable to cover the damage and diseases occurring throughout the body, resulting in worsening of diseases or aging. Stem cells administered in stem cell therapy patrol the body through the bloodstream, naturally gathering at damaged or diseased sites, and exerting an effect called the “homing effect” that promotes healing by acting on cells. Stem cell therapy for diabetic complications using the stem cell supernatant method “SGF” shows effectiveness in preventing complications by repairing blood vessels through the homing effect.
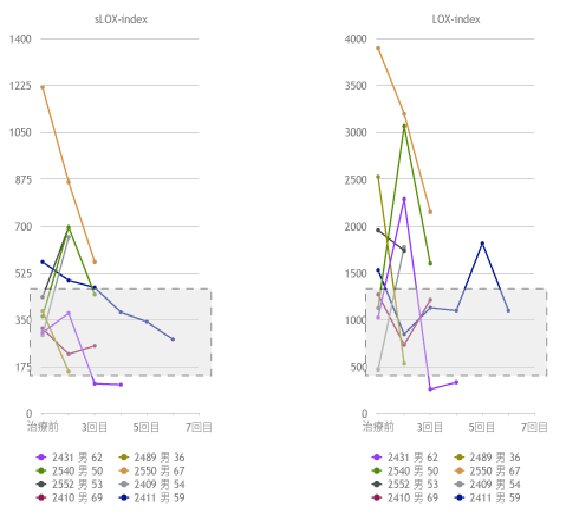
Based on the examination results of the LOX-index (a risk factor for stroke and myocardial infarction, which are complications of diabetes), vascular repair is observed, and there is also a tendency for improvement in creatinine levels, an indicator of kidney function.
According to an article by the International Society for Stem Cell Research, treatments utilizing the “homing” property of stem cells are actually being performed in regenerative medicine.
While some are still under development, here are four specific examples of regenerative medicine utilizing “homing”:
- Stroke
Stroke is caused by the occlusion of blood vessels in the brain.
When blood vessels in the brain are occluded, the supply of oxygen and glucose becomes impossible, leading to the death of brain cells.
Depending on the location of the occluded blood vessels or the affected area of the brain, paralysis, language disorders, and consciousness disorders may occur.
Until now, it was said that “brain cells that have died due to injury cannot return to their original state.”
Therefore, it has been said that the treatment of stroke is a race against time in order to stop the disability early and minimize the aftereffects.
However, recent research has revealed that the regeneration of damaged brain cells is possible with stem cell therapy, and clinical trials are underway.
This treatment uses marrow-derived or adipose-derived stem cells.
Mesenchymal cells are collected and cultured from the patient’s own bone marrow or adipose tissue, and stem cells are administered intravenously.
It is expected that they will be transported to the damaged brain cells by homing, leading to improvement of the stroke itself and reduction of sequelae.
2.Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a disease in which muscles throughout the body gradually weaken. It starts with symptoms such as numbness in the limbs and progresses to the point where the body cannot move gradually.
Motor neurons are impaired, and eventually swallowing function disappears, making breathing impossible. The cause is unknown, and no treatment has been established.
In such circumstances, stem cell therapy is expected.
It has been found that intravenous administration of stem cells acts on damaged nerves and can improve symptoms or delay progression.
3.Spinal Cord Injury
When the spinal cord is damaged by external stimuli such as accidents, it causes paralysis and sensory abnormalities.
When complete paralysis occurs, the lower and upper limbs cannot move at all, and sensation is lost. Like the brain, once the cells of the spinal cord are damaged, they do not return to their original state, and effective treatments have not been found at this point.
Stem cell therapy has also been found to be effective for spinal cord injuries.
When cultured stem cells are administered intravenously, they act on damaged stem cells and are expected to regenerate the impaired spinal cord.
Diabetes
Diabetes is deeply associated with a hormone called “insulin” secreted from the pancreas.
However, when the function of insulin deteriorates due to some reason, or when insulin cannot be secreted properly, blood sugar levels remain high.
This condition is called diabetes.
Initially, it is often asymptomatic, but as the symptoms progress, it can lead to various complications.
Diabetic retinopathy increases the risk of blindness.
Diabetic neuropathy can lead to impaired peripheral blood flow, sometimes requiring amputation of the feet or hands.
Stem cell therapy is also expected to restore pancreatic function in cases of pancreatic dysfunction.
In addition, treatment methods utilizing “homing” are being implemented in medical institutions.
Quotation: Regenerative medicine utilizing the property of stem cells called “homing” / International Society for Stem Cell Research
URL:https://stemcells.or.jp/homing-effect/


